Idarubicine
Apparence
(Redirigé depuis C26H27NO9)
| Idarubicine | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
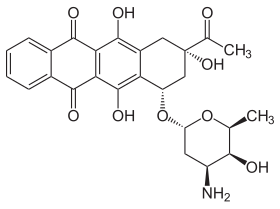
| Nom UICPA | (1S,3S)-3-acétyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotétracén-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxo-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside |
| No CAS | |
| Code ATC | L01 |
| PubChem | 42890 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C26H27NO9 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 497,493 9 ± 0,025 6 g/mol C 62,77 %, H 5,47 %, N 2,82 %, O 28,94 %, |
| Écotoxicologie | |
| DL50 | 16 mg/kg (souris, oral)[2] 4 mg/kg (souris, i.v.)[2] 3 mg/kg (souris, i.p.)[2] |
| LogP | 2.100 (octanol/eau)[2] |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
L'idarubicine ou 4-déméthoxydaunorubicine est un anticancéreux de type anthracycline. Elle s'insère dans l'ADN et l'empêche de se dérouler en interférant avec l'enzyme topoisomérase II. C'est un analogue de la daunorubicine, mais l'absence de groupe méthoxy accroît sa liposolubilité et son absorption cellulaire[RCP 1].
Indications
[modifier | modifier le code]L'idarubicine est indiquée dans le traitement des leucémies :
- en association avec la cytarabine en 1re ligne d’induction de la rémission chez des enfants non précédemment traités et atteints de leucémie aiguë myéloïde (LAM)[RCP 2];
- leucémies aiguës lymphoblastiques en rechute;
- dans le traitement de la leucémie aiguë promyélocytaire en association avec l'acide tout-trans rétinoïque (protocole AIDA), indication[3] ; l'usage des anthracyclines dans cette indication se réduit au profit du trioxyde d'arsenic.
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]RCP
[modifier | modifier le code]- « RCP américain Idamycin », sur pfizer.com (consulté le )
- « Résumé des caractéristiques du produit - ZAVEDOS 10 mg/10 ml, solution pour perfusion - Base de données publique des médicaments » (consulté le )
Sources
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) « Idarubicine », sur ChemIDplus.
- (en) for the Italian GIMEMA Cooperative Group, « Front-line treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with AIDA induction followed by risk-adapted consolidation for adults younger than 61 years: results of the AIDA-2000 trial of the GIMEMA Group », Blood, American Society of Hematology, vol. 116, no 17, , p. 3171-3179 (ISSN 1528-0020, DOI 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276196, résumé, lire en ligne)
