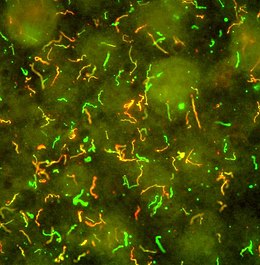
Spirochétose
Apparence
Spirochétose
Forme libre, spiralée de Borrelia burgdorferi, l'un des principaux agents de la maladie de Lyme, le premier à avoir été identifié.
| Causes | Infection ou Spirochaetales |
|---|
| Spécialité | Infectiologie |
|---|
| CIM-10 | A69.9 |
|---|---|
| CIM-9 | 104.8 |
| MeSH | D013145 |
La spirochétose est une maladie infectieuse causée par l'un des spirochètes pathogènes (bactéries hélicoïdales pouvant aussi prendre d'autres formes, kystiques lorsqu'elles sont en situation de stress[1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10],[11]).
Exemples
[modifier | modifier le code]Les spirochétoses les plus connues sont la leptospirose, les borrélioses (maladie de Lyme notamment), le pian et la syphilis sont des spirochétoses.
Voir aussi
[modifier | modifier le code]Articles connexes
[modifier | modifier le code]Liens externes
[modifier | modifier le code]Bibliographie
[modifier | modifier le code]Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Alban PS, Johnson PW, Nelson DR (2000) Serum-starvation-induced changes in protein synthesis and morphology of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiology 146:119–127.
- Gruntar I, Malovrh T, Murgia R, Cinco M (2001) Conversion of Borrelia garinii cystic forms to motile spirochetes in vivo. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 109:383–388.
- Brorson Ø, Brorson SH (1998) In vitro conversion of Borrelia burgdorferi to cystic forms in spinal fluid, and transformation to mobile spirochetes by incubation in BSK-H medium. Infection 26:44 –50.
- Dever LL, Jorgensen JH, Barbour AG (1993) In vitro activity of vancomycin against the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37:1115–1121.
- Dubinina G, Grabovich M, Leshcheva N, Gavrish E, Rainey FA (2009) Spirochaeta perfilievii sp. nov., a novel oxygen-tolerant, sulfide oxidizing, sulfur and thiosulfate- reducing spirochete isolated from a saline spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, in press.
- Hampp EG (1951) Further studies on the significance of spirochetal granules. J Bacteriol 62:347–349.
- Hindle E (1911) On the life-cycle of Spirochaeta gallinarum. Parasitology 4:463– 477.
- Kersten A, Poitschek C, Rauch S, Aberer E (1995) Effects of penicillin, ceftriaxone, and doxycycline on morphology of Borrelia burgdorferi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:1127–1133.
- Kraiczy P, et al. (2001) In vitro activities of fluoroquinolones against the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:2486 –2494.
- Murgia R, Piazzetta C, Cinco M (2002) Cystic forms of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: Induction, development, and the role of RpoS. Wien Klin Wochenschr 114:574 –579.
- Brorson Ø, Brorson S.H, Scythes J, MacAllister J, Wier A & Margulis L (2009) Destruction of spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi round-body propagules (RBs) by the antibiotic tigecycline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 18656–18661. (résumé)