Quinnipiac
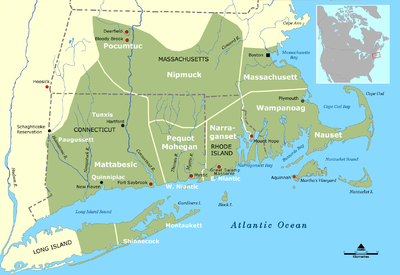
La tribu Quinnipiac, parfois Quinnipiack est le nom européen de la tribu amérindienne qui se nommait Eansketambawg (littéralement « peuple originel »). La tribu, qui appartient aux peuples algonquiens, vivait dans la région du Connecticut à l'arrivée des premiers colons européens. Ils employaient la langue Quiripi.
Étymologie
[modifier | modifier le code]
La tribu porte le même nom que le cours d'eau de la région. Le fleuve Quinnipiac s'écoule du nord au sud entre Farmington jusqu'au port de New Haven. D'une longueur de 61 km, son nom signifie « Terre de l'eau étendue ». La tribu disposait de plusieurs villages le long de ce cours d'eau. Le Sleeping Giant (littéralement « Géant endormi »), une montagne, était un lieu sacré pour cette tribu. Dans leur mythologie, ce rocher était le corps pétrifié d'un héros, le géant de pierre Hobbomock.
Histoire
[modifier | modifier le code]La tribu est considérée comme étant la première tribu amérindienne à avoir été placée dans une réserve amérindienne (par les Anglais dès 1638)[1] à la suite de la signature du premier traité d'une longue série entre les colons européens et les peuplades amérindiennes d'Amérique du Nord. Ces réserves étaient alors situées à Branford, Madison, Derby et Farmington[2].
J.H. Trumbull est le premier à découvrir que la communauté amérindienne Quinnipiac découverte par les premiers Européens n'est qu'une petite partie d'une plus grande tribu[3]. Blair Rudes découvre que le groupe dialectal des Algonquins de l'est s'étend jusque l'Hudson à l'ouest[4]. Depuis 1997, de nouvelles études tendent à penser que la tribu était basée dans toute la région du Connecticut, l'est de l'État de New York, le nord du New Jersey et la moitié de l'île de Long Island (avant la migration dans la région des tribus Pequot/Mohegan)[5].
Annexes
[modifier | modifier le code]Bibliographie
[modifier | modifier le code]En ligne
[modifier | modifier le code]- (en) ACQTC ON-LINE: http://www.acqtc.com.
- (en) We the People Called Quinnipiac, QTC Press e-media e-book on CD-ROM (available through ACQTC, see http://acqtc.com/Store/HomePage)
- (en) Setting the Record Straight: A Linguistic-Ethnographic Study of the True Identity of the Quinnipiac/Quiripi/Renapi Nation Structure par Iron Thunderhorse, http://www.acqtc.com/Articles/SettingtheRecordStraight
- (en) Quinnipiac River History (« http://coldspringschool.org/griver/oldeq.htm »(Archive.org • Wikiwix • Archive.is • Google • Que faire ?))
- (en) The City of New Haven — Land of the Quinnipiac (« http://www.yale,edu/ynhti/curriculum/units/1997/4/97.04.01.x.html »(Archive.org • Wikiwix • Archive.is • Google • Que faire ?))
- (en) Quinnipiac University — History and Mission Statement (« http://quinnipiac.edu/xioii.xml »(Archive.org • Wikiwix • Archive.is • Google • Que faire ?))
- (en) Quinnipiac Dawnland Museum, Archives and Library (http://acqtc.com/NewsEvents/200606)
- (en) Benjamin BRETON (2008) The Quinnipiac: New Haven’s First Inhabitants. Communication on Contemporary Anthropology 2:e12. (« http://comonca.org/2008012.aspx »(Archive.org • Wikiwix • Archive.is • Google • Que faire ?))
Livres
[modifier | modifier le code]- (en) The Complete Language Guide for Learning, Speaking, and Writing the PEA-A WAMPANO-QUIRIPI R-DIALECT, 2007 revised ed, QTC Press/ACLI Series, ACQTC, Inc. 201 Church Street, Milltown, IN 47145.
- (en) The Quinnipiac of New England par Iron Thunderhorse dans Whispering Wind, Vol. 32, No. 5, 2002.
- (en) Cultural Conflict in Southern New England: A History of the Quinnipiac Indians by John Menta, Yale Press, New Haven. CT.
- (en) Some Helps for the Indians 1658 Bilingual Catechism, par Rev. Abraham Pierson, reprinted dans Language and Lore of the Long Island Indians Readings in Long Island Archaeology and Ethnohistory, Vol. IV, 1980. Stony Brook, NY, Suffolk County Archaeological Association.
- (en) East Rock (Wappintumpseck): A Sacred Landmark In the Traditions of the Quinnipiac and Its Relationship to the Algonquian Ethos par Iron Thunderhorse, 1996. Paper submitted to Connecticut Historical Commission and University of Connecticut at Storrs, CT.
- (en) The Strange Case of Nepaupuck: Warrior or War Criminal? dans le Journal of the New Haven Colony Historical Society, Vol. 33 (2) 12-17, 1987, par John Menta.
- (en) The Quinnipiac Reservation: Land and Tribal Identity, par Richard Carlson dans Rooted Like the Ash Trees, Naugatuck, CT: Eagle Wing Press, 1987-1988.
- (en) Shaumpishuh, ‘Squaw Sachem’ of the Quinnipiac Indians, par John Menta dans Artifacts, 1988, Vol. 16, No. 3-4, pp. 32-37.
- (en) Resurrecting Wampano (Quiripi) from the Dead: Phonological Preliminaries par Blair A. Rudes, dans Anthropological Linguistics, Vol. 39, No. 1, Spring 1997.
- (en) Indian Names of Places, etc. In and on the Borders of Connecticut with Interpretations of Some of Them, par James Hammond Trumbull, 1881 (reprinted 1974 by Archon Books).
- (en) The intricate nature of sachemdoms par Iron Thunderhorse dans Branford Review, 9-7-02.
- (en) Itineraries and Memoirs of Ezra Stiles, 1760-1762. Beineke Rare Books Library, New Haven, CT.
- (en) Native People of Southern New England, 1500-1650, par Kathleen J. Bragdon, Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1996.
- (en) Algonquians of the East, Time-Life Books, 1995.
- (en) The New England Indians, 2nd ed. An Illustrated SourceBook of Authentic Details of Everyday Indian Life par C. Keith Wilbur, Globe-Pequot Press.
- (en) Wampano: Algonquian Dawnlanders of Southwestern New England, 1500-2000, par Iron Thunderhorse. Birdstone Publishers, Institute for American Indian Studies (reprint by QTC Press Archives series, ACQTC, Inc. 201 Church Street, Milltown, IN 47145)
- (en) Quinnipiac Lunar and Ceremonial Calendar, 2003-2004, par Iron and Ruth Thunderhorse, QTC Press, 2003, ACQTC, Inc., 201 Church Street, Milltown, IN 47145.
Références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Richard Carlson, “The Quinnipiac Reservation,” Rooted Like the Ash Trees, Eagle Wing Press, 1987.
- Iron Thunderhorse, “The ‘Other’ Quinnipiac Reservations”, Branford Review, April 26, 2003.
- J.H. Trumbull, Indian Names of Places, In and On the Borders of Connecticut, Hartford, CT 1881 (reprinted 1974 by Archon Books, the Shoestring Press, Inc., Hamden. Also see Trumbull’s Introduction to 1658 Pierson Catechism, in 1895 CHS Collections.
- Blair Rudes, “Resurrecting Wampano (Quiripi) from the Dead, Phonological Preliminaries,” Anthropological Linguistics, Vol. 39. No. 1, Spring 1997
- John Menta, “Shaumpishuh, ‘Squaw Sachem’ of the Quinnipiac Indians” in ARTIFACTS, Vol. 16, No. 3-4:32-27, 1988 and Iron Thunderhorse, “Setting the Record Straight: A Linguistic-Ethnographic Study of the True Identity of the Quinnipiac/Quiripi/Renapi Nation Structure.” 2007 [1]
