Varacine
| Varacine | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
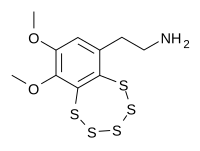
| Nom UICPA | 2-(6,7-diméthoxy-1,2,3,4,5-benzopentathiépin-9-yl)éthanamine |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 179269 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C10H3NO2S5 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 329,461 ± 0,034 g/mol C 36,46 %, H 0,92 %, N 4,25 %, O 9,71 %, S 48,66 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
La varacine est un composé bicyclique organo-sulfuré trouvé originellement chez les ascidies du genre Polycitor, des organismes marins du sous-embranchement des tuniciers (Tunicata)[2].
Cette molécule contient un cycle pentathiépine très inhabituel qui réagit avec l'ADN. La varacine et des analogues synthétiques ont été étudiés du point de vue de leurs propriétés antibactériennes et antitumorales[3],[4].
Notes et références[modifier | modifier le code]
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Varacin and three new marine antimicrobial polysulfides from the far-eastern ascidian Polycitor sp., Makarieva TN; Stonik VA; Dmitrenok AS; Grebnev BB; Isakov VV; Rebachyk NM; Rashkes YW; Journal of Natural Products, 1995, vol. 58(2), p. 254-8. .
- On the origin of cytotoxicity of the natural product varacin. A novel example of a pentathiepin reaction that provides evidence for a triatomic sulfur intermediate., Greer A; Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, vol.123(42), p. 10379-86. .
- The role of amine in the mechanism of pentathiepin (polysulfur) antitumor agents, Brzostowska EM; Greer A; Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, vol. 125(2), p. 396-404.
- (en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé « Varacin » (voir la liste des auteurs).
