U Antliae
U Antliae
Image ALMA des enveloppes de poussières autour de U Antliae.
| Ascension droite | 10h 35m 12,852s[1] |
|---|---|
| Déclinaison | −39° 33′ 45,32″[1] |
| Constellation | Machine pneumatique |
| Magnitude apparente | 5,27 - 6,04[2] |
Localisation dans la constellation : Machine pneumatique | |
| Type spectral | C5,3[3] |
|---|---|
| Indice U-B | 7,10[4] |
| Indice B-V | 2,84[4] |
| Variabilité | LB[5] |
| Vitesse radiale | 41,00 km/s[6] |
|---|---|
| Mouvement propre |
μα = −31,372 ± 0,228 mas/a[7] μδ = 2,371 ± 0,267 mas/a[7] |
| Parallaxe | 3,571 7 ± 0,204 3 mas[7] |
| Distance | 202 ± 2 a.l. (∼ 61,9 pc) |
| Magnitude absolue | −5,22[8] |
| Rayon | 325 R☉[9] |
|---|---|
| Luminosité | 8 000 L☉[10] |
| Température | 2 000 K[10] |
Désignations
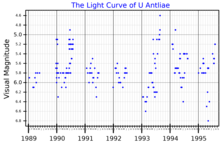
U Antliae est une étoile carbonée rouge de type C et une variable irrégulière, dont la magnitude évolue entre 5,27 et 6,04[2]. Située à 910 ± 50 a.l. (∼ 279 pc)[7], elle est 5 819 fois plus lumineuse que le Soleil[12]. Elle est entourée de deux enveloppes de poussières, dont on estime l'éjection il y a 14 000 et 10 000 ans[13].
Notes et références[modifier | modifier le code]
- (en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé « U Antliae » (voir la liste des auteurs).
- (en) F. van Leeuwen, « Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 474, no 2, , p. 653–664 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode 2007A&A...474..653V, arXiv 0708.1752)
- Sebastian Otero, « U Antliae », sur The International Variable Star Index, American Association of Variable Star Observers, (consulté le )
- (en) Y. Yamashita, « The C-classification of spectra of carbon stars. II », Tokyo, vol. 15, , p. 47 (Bibcode 1975AnTok..15...47Y)
- (en) J. R. Ducati, « VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system », CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues, vol. 2237, (Bibcode 2002yCat.2237....0D)
- (en) N. N. Samus, O. V. Durlevich et al., « VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013) », VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs. Originally published in: 2009yCat....102025S, vol. 1, (Bibcode 2009yCat....102025S)
- (en) G. A. Gontcharov, « Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system », Astronomy Letters, vol. 32, no 11, , p. 759 (DOI 10.1134/S1063773706110065, Bibcode 2006AstL...32..759G, arXiv 1606.08053)
- (en) A. G. A. Brown et al. (Gaia collaboration), « Gaia Data Release 2 : Summary of the contents and survey properties », Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol. 616, , article no A1 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051, Bibcode 2018A&A...616A...1G, arXiv 1804.09365). Notice Gaia DR2 pour cette source sur VizieR.
- (en) Guandalini, R. et Cristallo, S., « Luminosities of carbon-rich asymptotic giant branch stars in the Milky Way », Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol. 555, , p. 7, article no A120 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/201321225, Bibcode 2013A&A...555A.120G, arXiv 1305.4203)
- (en) E. De Beck, L. Decin, A. De Koter, K. Justtanont, T. Verhoelst, F. Kemper et K. M. Menten, « Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles. II. CO line survey of evolved stars: Derivation of mass-loss rate formulae », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 523, , A18 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/200913771, Bibcode 2010A&A...523A..18D, arXiv 1008.1083)
- (en) F. Kerschbaum, D. Ladjal, R. Ottensamer, M. A. T. Groenewegen, M. Mecina, J. A. D. L. Blommaert, B. Baumann, L. Decin, B. Vandenbussche, C. Waelkens, T. Posch, E. Huygen, W. De Meester, S. Regibo, P. Royer, K. Exter et C. Jean, « The detached dust shells of AQ Andromedae, U Antliae, and TT Cygni », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 518, , p. L140 (DOI 10.1051/0004-6361/201014633, Bibcode 2010A&A...518L.140K, arXiv 1005.2689)
- (en) V* U Ant -- Carbon Star sur la base de données Simbad du Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- (en) I. McDonald, A. A. Zijlstra et M. L. Boyer, « Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars », Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, vol. 427, no 1, , p. 343–57 (DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, Bibcode 2012MNRAS.427..343M, arXiv 1208.2037)
- (en) H. Izumiura, L. B. F. M. Waters, T. de Jong, C. Loup, Tj. R. Bontekoe et D. J. M. Kester, « A double dust shell surrounding the carbon star U Antliae », Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 323, , p. 449–60 (Bibcode 1997A&A...323..449I)
- (en) « Download Data », sur aavso.org, AAVSO (consulté le )


